728x90
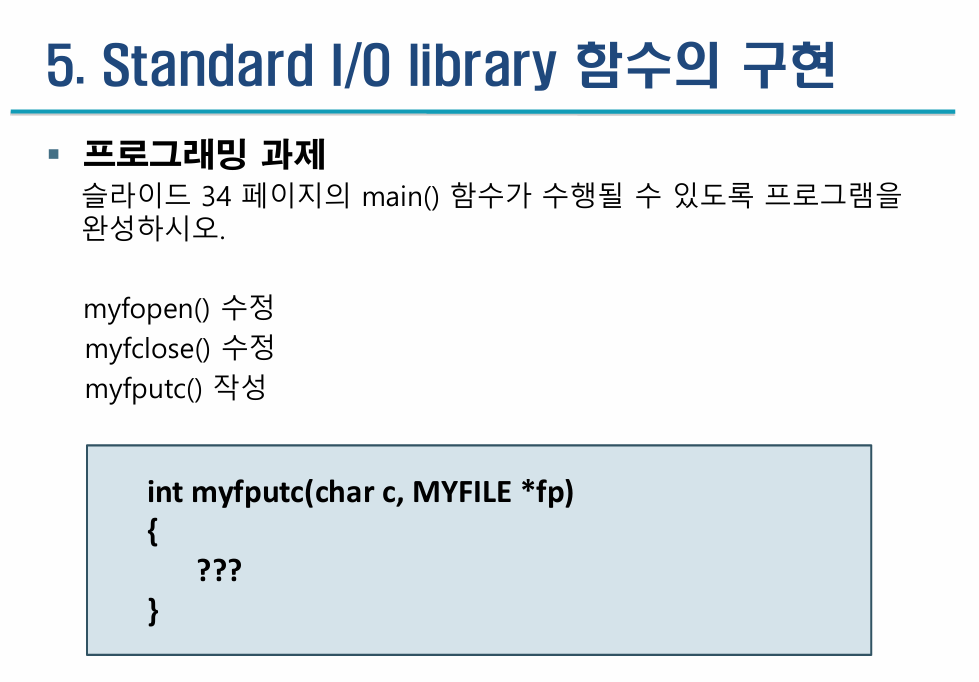
6주차 강의자료 34 페이지의 main() 함수가 수행될 수 있도록 필요한 함수를 수정, 추가하여 프로그램을 완성하시오.
// mystdio.c
#include "mystdio.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
MYFILE *myfopen(char *file, char *mode)
{
MYFILE *fp = (MYFILE *)malloc(sizeof(MYFILE));
if (fp != NULL) {
if (strcmp(mode, "r") == 0) {
if ((fp->fd = open(file, O_RDONLY)) < 0) {
free(fp);
return NULL;
}
fp->mode = READ_MODE;
fp->length = fp->offset = 0;
}
else if (strcmp(mode, "w") == 0) { //쓰기 모드
if ((fp->fd = open(file, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0644)) < 0) {
free(fp);
return NULL;
}
fp->mode = WRITE_MODE;
fp->length = BUFSIZE; // 버퍼 크기 설정
fp->offset = 0; // 버퍼 시작위치 0
}
else {
fprintf(stderr, "not supported mode: %s\n", mode);
free(fp);
return NULL;
}
}
return fp;
}
char myfgetc(MYFILE *fp)
{
if (fp == NULL) return EOF;
if (fp->offset == fp->length) {
if ((fp->length = read(fp->fd, fp->buf, BUFSIZE)) < 1)
return EOF;
fp->offset = 0;
}
return fp->buf[fp->offset++];
}
int myfputc(char c, MYFILE *fp)
{
if (fp == NULL) return EOF;
// Length == Offset이면 버퍼가 가득 찬 상태
if (fp->offset == fp->length) {
if (write(fp->fd, fp->buf, BUFSIZE) != BUFSIZE) {
// write 실패
return EOF;
}
fp->offset = 0; // 버퍼를 비웠으니 offset 0으로 초기화
}
// 버퍼에 문자 저장
fp->buf[fp->offset++] = c;
return (unsigned char)c;
}
int myfclose(MYFILE *fp) {
if (fp == NULL) return EOF;
if (fp->mode == WRITE_MODE && fp->offset > 0) {
if (write(fp->fd, fp->buf, fp->offset) != fp->offset) {
free(fp);
return EOF;
}
}
if (close(fp->fd) < 0) {
free(fp);
return EOF;
}
free(fp);
return 0;
}728x90
'{Lecture} > System Programming' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [시스템 프로그래밍] 명령어 정리 (0) | 2025.04.19 |
|---|---|
| [시스템 프로그래밍] 3장 파일다루기 Part 1 (0) | 2025.04.01 |
| [시스템 프로그래밍] 2장 파일 시스템 정리 (0) | 2025.04.01 |
| [시스템 프로그래밍] LINUX 소개 Part 2 (0) | 2025.03.25 |
| [시스템 프로그래밍] LINUX 소개 Part 1 (0) | 2025.03.16 |

